
#Root word vs word root plus
Distinguishing between roots (single morphemes) and bases (root morpheme plus one or more affixes, or compounds) seems like a goodly distinction, though perhaps overkill for English morphology. In English grammar, a root word is the basic lexical unit of a word that carries its core meaning. There a lexeme (aka lexical item, word) like man consists of a single morpheme, though come to think of it the Latin nominative singular vir 'man' has no explicit nominitival desinence, as rosa (i.e., the - a) does). The problem may be with less inflected languages, like English or Chinese.
#Root word vs word root free
In the study of morphology, there is a difference between free and bound morphemes: free ones can stand on their own, but bound ones are usually affixes, though some like the rasp in raspberry are not. The former are usually called derivational morphemes (they change the meaning), and the latter inflectional (they indicate the syntactic relationships between words in a phrase).

Otherwise, it may define whether the word is a noun, verb, or adjective.įor more on medical terminology, see OpenMD's Introduction to Medical Terminology.In describing inflected languages, like Latin, Greek, or Sanskrit, a distinction between affixes (pre-, in-, and suffixes) and desinences (grammatical endings) is usually made.

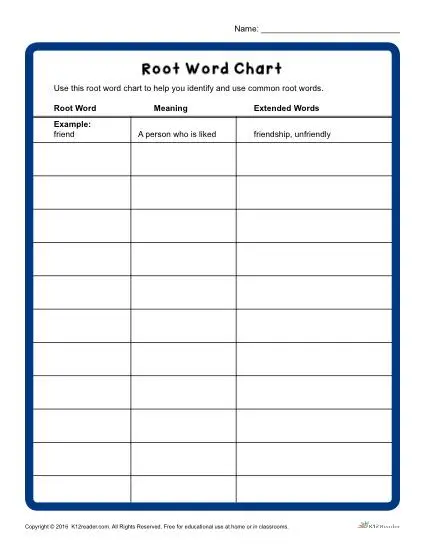
Three standard word elements-roots, prefixes, and suffixes-are used to construct most medical terms. Understanding the meanings of common roots can help you work out the meanings of new words as you encounter them.
In traditional root words, these words come from Latin and Greek, and typically do not stand alone as a complete word. The Student Copy doesnt have the answer slide on it if you dont want students to have the answers in the same file.It also contains a Google form. A root word is a word or word part that forms the basis of new words through the addition of prefixes and suffixes. The complete file contains the word sort and the answers as a separate Google Slide in one file. For example, the word arthritis is based on the Greek word arthron ( joint) + the Greek ending itis ( inflammation of). This is a word sort for latin roots (dic, aud, vis).The file contains 2 Google Slide files and 1 Google Form. This is especially true of medical terms, which usually are based on Greek or Latin words. 1 day ago &0183 &32 The word was used to describe Black people on the gov.uk site. When available, the original Greek or Latin term is provided in parentheses after the English definition. You probably already know that most English words are derived from some other languages, such as Greek, Latin, French, or German. OpenMD’s index includes 750 common roots, prefixes, and suffixes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
